Using Quality Control Tools to Strengthen Business Performance
In today’s highly competitive market, ensuring product or service quality is a key factor in building customer trust and business success. To achieve this, companies rely on structured methods to monitor and improve processes. Quality Control Tools serve as the foundation for identifying problems, improving workflows, and delivering consistent outcomes.
What Are Quality Control Tools?
Quality Control Tools are techniques used to collect data, analyze performance, and resolve quality-related issues in a systematic way. These tools help organizations gain insights into their operations, reduce defects, and maintain high standards throughout production or service delivery.
Why Quality Control Tools Are Essential for Success
Using Quality Control Tools allows businesses to detect problems early, prevent recurring issues, and make data-driven decisions. These tools support continuous improvement by revealing inefficiencies and helping teams implement solutions. When used consistently, they lead to better products, fewer complaints, and more efficient operations.
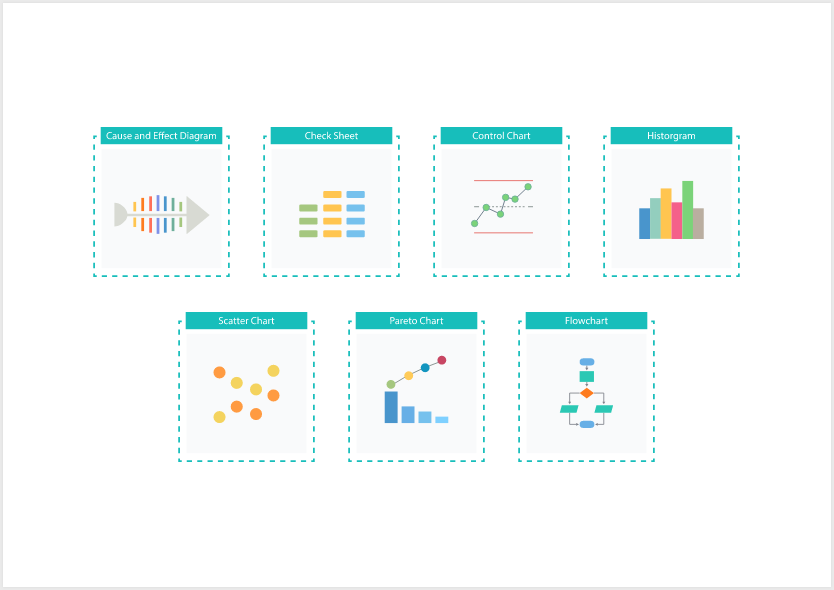
The Seven Fundamental Quality Control Tools
Here are the seven core Quality Control Tools that every quality-focused organization should know and apply:
1. Flowchart
Flowcharts visually map out processes, helping teams understand the sequence of steps and spot areas where delays or errors may occur.
2. Check Sheet
Check sheets are used for real-time data collection, such as tracking the frequency of defects, errors, or other important events.
3. Cause-and-Effect Diagram
Also known as the fishbone or Ishikawa diagram, this tool helps identify all possible causes of a problem and organize them into logical categories.
4. Histogram
Histograms show the distribution of data and are useful for identifying variations in a process that may impact quality.
5. Pareto Chart
This chart follows the 80/20 principle to highlight the most common causes of issues, helping teams prioritize which problems to tackle first.
6. Control Chart
Control charts monitor a process over time and signal when variations fall outside acceptable limits, prompting corrective action.
7. Scatter Diagram
Scatter diagrams help analyze the relationship between two variables to determine if one factor may be influencing another.
Benefits of Implementing Quality Control Tools
When businesses apply these Quality Control Tools, they benefit from improved efficiency, lower error rates, and higher customer satisfaction. These tools also promote better teamwork, greater transparency, and a culture of ongoing improvement.
Conclusion
Quality Control Tools are critical components of effective quality management. They help businesses move from guesswork to data-driven decision-making and ensure processes stay aligned with performance goals. By adopting these tools, organizations can not only meet expectations but consistently exceed them, setting the stage for long-term growth and success.