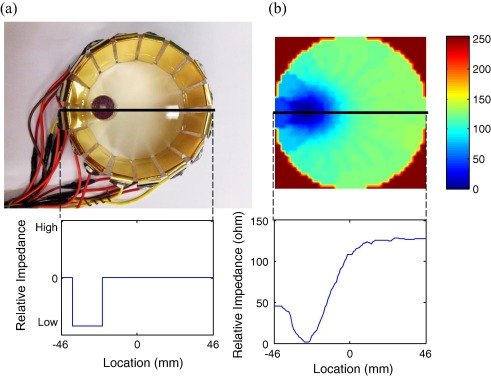
Understanding the Basics of Electrical Impedance Tomography
Electrical Impedance Tomography (EIT) is a non-invasive imaging technique that has gained significant attention in various fields, including medical diagnostics, industrial processes, and environmental monitoring. This innovative technology allows researchers and professionals to visualize and analyze the distribution of electrical impedance within a target object or medium. In this article, we will explore the fundamental principles, applications, and potential benefits of Electrical Impedance Tomography.
What is Electrical Impedance Tomography?
Electrical Impedance Tomography is a medical imaging technique that involves the measurement of electrical impedance at the body’s surface to create images of internal structures. Unlike traditional imaging modalities such as X-rays or CT scans, EIT does not use ionizing radiation, making it a safer option for continuous monitoring and repeated imaging.
The basic concept behind EIT is to inject a small electric current into the target object or medium and measure the resulting voltage distribution on its surface. By analyzing the changes in electrical impedance, EIT algorithms reconstruct an image that represents the internal conductivity distribution of the object.
How Does EIT Work?
EIT systems typically consist of an array of electrodes placed on the surface of the object or body under examination. These electrodes are used to both inject electrical currents and measure voltages. The applied currents cause a potential difference, and the resulting voltage distribution is measured. The variations in voltage provide information about the electrical properties of the internal structures.
Sophisticated algorithms then process the acquired data to reconstruct a two-dimensional or three-dimensional image of the electrical conductivity distribution within the target. This reconstructed image helps visualize the internal composition and can be used for diagnostic purposes in medical applications, such as lung imaging or monitoring brain activity.
Applications of Electrical Impedance Tomography
Medical Imaging
One of the primary applications of EIT is in the field of medical imaging. EIT has shown promise in various clinical areas, including:
- Lung Imaging: EIT is used for real-time monitoring of ventilation and lung perfusion, making it valuable in critical care settings.
- Brain Monitoring: EIT can be applied to monitor cerebral blood flow and detect abnormalities in brain activity, aiding in the diagnosis of neurological disorders.
- Breast Imaging: Research is ongoing to explore the use of EIT as a complementary tool for breast cancer detection.
Industrial Processes
EIT finds applications in monitoring and control within industrial processes, such as:
- Process Imaging: EIT can be used to visualize the distribution of materials in industrial processes, aiding in quality control and optimization.
- Pipeline Monitoring: EIT is employed to detect and locate anomalies in pipelines, ensuring the integrity and safety of the infrastructure.
Environmental Monitoring
EIT can be utilized for environmental studies, including:
- Soil Moisture Measurement: EIT helps in assessing soil moisture content, crucial for agriculture and environmental conservation.
- Groundwater Monitoring: EIT is applied to monitor changes in groundwater levels and assess the impact of human activities on aquifers.
Potential Benefits of EIT
- Non-invasive Nature: EIT does not involve ionizing radiation, making it a safer option for continuous monitoring, especially in medical applications.
- Real-time Imaging: EIT provides real-time imaging capabilities, allowing for dynamic monitoring and immediate feedback.
- Cost-effectiveness: Compared to some traditional imaging techniques, EIT can be more cost-effective, making it an attractive option for certain applications.
In conclusion, Electrical Impedance Tomography represents a promising imaging technique with diverse applications. Its non-invasive nature, real-time imaging capabilities, and cost-effectiveness make it an attractive option for various fields, from medical diagnostics to industrial processes and environmental monitoring. As technology continues to advance, EIT is likely to play an increasingly significant role in improving imaging capabilities and contributing to advancements in science and industry.